定义及分析
Contrastive loss 即对比损失,其表达式为:
其中,
-
y表示标签值,取值为1,0; -
margin是人为定义的边界距离; -
d表示两个样本的
欧氏距离
输入为 ( dataA, dataB, label )
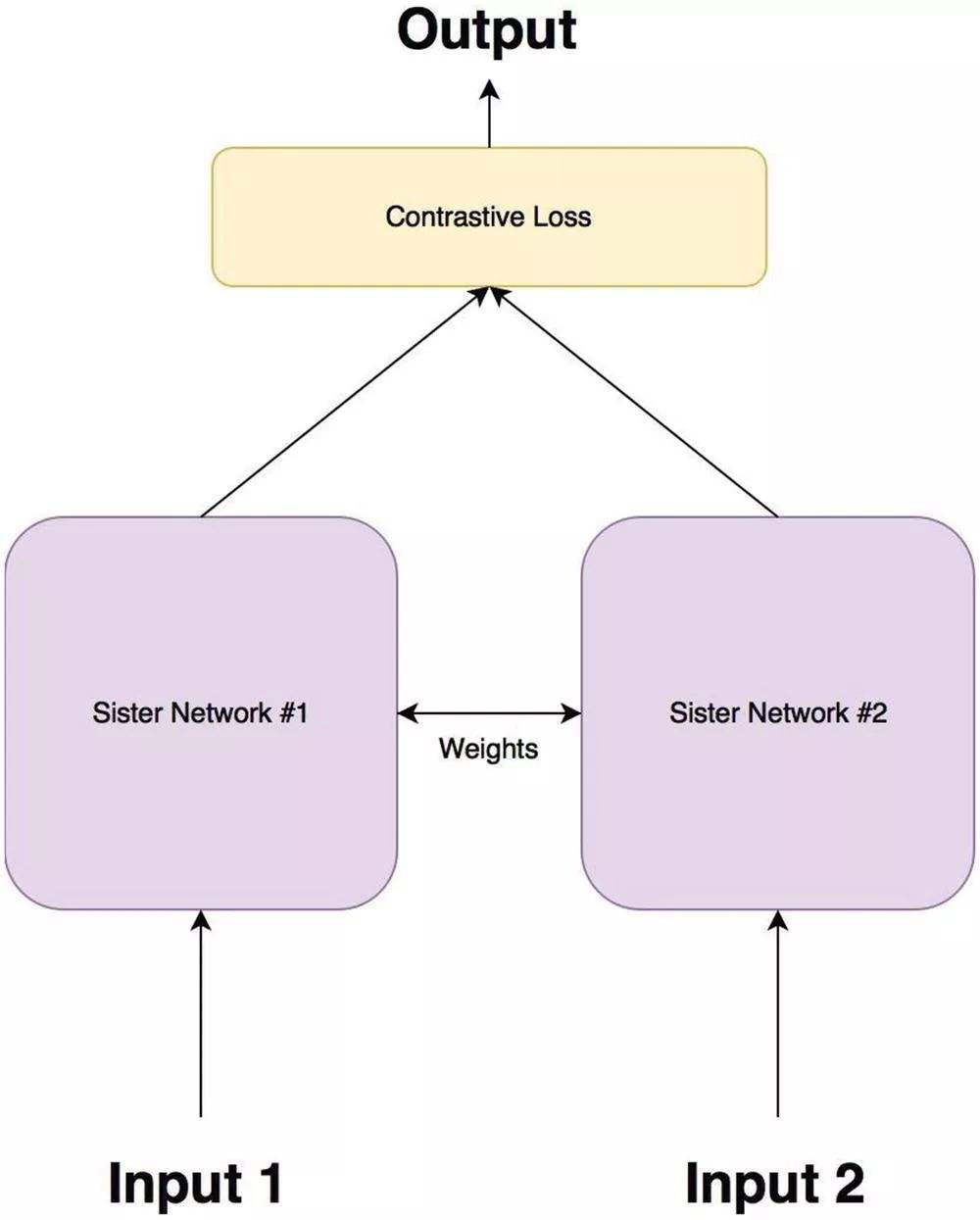
该损失函数可以有效的处理孪生神经网络中的paired data的关系,具体逻辑是:
- 若一对数据是同一组,那么
label = 1即y = 1,只有前半部分起作用,后半部分值为0;此时最小化loss, 两者的欧氏距离变小,就会使两者更相似; - 若一对数据非同一组,那么
label = 0即y = 0, 只有后半部分起作用,前半部分值为0,此时最小化损失函数,即最小化margin - d, 就等于最大化d,即两者的欧氏距离变大,更不相似
梯度求解
y = 1时,
此处省略,以后补充
代码实现
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# # @Time : 2020/5/17 上午 11:19
# # @Author : fry
# @FileName: clac.py
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'''
计算欧式距离
'''
import torch
def euclidean_dist_vector(x, y):
'''
:param x: [100]
:param y: [100]
:return:
'''
dist = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(torch.pow((x-y), 2)))
return dist
def euclidean_dist(x, y):
"""
Args:
x: pytorch Variable, with shape [m, d]
y: pytorch Variable, with shape [n, d]
Returns:
dist: pytorch Variable, with shape [m, n]
"""
m, n = x.size(0), y.size(0)
# xx经过pow()方法对每单个数据进行二次方操作后,在axis=1 方向(横向,就是第一列向最后一列的方向)加和,此时xx的shape为(m, 1),经过expand()方法,扩展n-1次,此时xx的shape为(m, n)
xx = torch.pow(x, 2).sum(1, keepdim=True).expand(m, n)
# yy会在最后进行转置的操作
yy = torch.pow(y, 2).sum(1, keepdim=True).expand(n, m).t()
dist = xx + yy
# torch.addmm(beta=1, input, alpha=1, mat1, mat2, out=None),这行表示的意思是dist - 2 * x * yT
dist.addmm_(1, -2, x, y.t())
# clamp()函数可以限定dist内元素的最大最小范围,dist最后开方,得到样本之间的距离矩阵
dist = dist.clamp(min=1e-12).sqrt() # for numerical stability
return dist
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# # @Time : 2020/5/11 下午 7:52
# # @Author : fry
# @FileName: MatchLoss.py
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from utils.clac import euclidean_dist,euclidean_dist_vector
# match loss function
class ContrastiveLoss(nn.Module):
"""
Contrastive loss function.
Based on:
"""
def __init__(self, margin=1.2):
super(ContrastiveLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
def check_type_forward(self, in_types):
assert len(in_types) == 3
#[1,1,10,10] [1,1,10,10] [10]
x0_type, x1_type, y_type = in_types
assert x0_type.size() == x1_type.shape
# assert x1_type.size()[1] == y_type.shape[0]
# assert x1_type.size()[0] > 0
assert x0_type.dim() == 4
assert x1_type.dim() == 4
# assert y_type.dim() == 1
def forward(self, x0, x1, y):
# self.check_type_forward((x0, x1, y))
data_1 = x0 # [1,10,10]
data_2 = x1 # [1,10,10]
# euclidian distance
distance = euclidean_dist_vector(data_1, data_2)
# distance = euclidean_dist(data_1, data_2)
md = self.margin - distance
dist = torch.clamp(md, min=0.0)
loss = y * torch.pow(distance, 2) + (1-y)*torch.pow(dist, 2)
loss = torch.mean(loss/2)
# loss = torch.sum(loss) / 2.0
return loss
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# citer = ContrastiveLoss()
# a = torch.randn(10,10)
# b = torch.randn(10,10)
# y = torch.ones(1)
# loss = citer(a,b,y)
# print(loss)